
The Complete Software Engineer Roadmap 2026: From Zero to Hired in 8 Months (No Degree Required)
This roadmap has placed 250+ complete beginners into software engineering roles in 2025 via [STEM Link](https://stemlink.online/products/bootcamps)**, bypassing the traditional path entirely. No CS degree required. No algorithms PhD needed. No leetcode grinding for 2 years.
The Complete Software Engineer Roadmap 2026: From Zero to Hired in 8 Months (No Degree Required)
Here's the truth universities and institutes don't want you to know: 78% of working software engineers say their degree was not the deciding factor for their actual job. Yet you're being sold on 4-year degrees costing LKR 20+ lakhs and really don't guarantee you job-readiness or a actual software engineering role.
This roadmap has placed 250+ complete beginners into software engineering roles in 2025 via STEM Link, bypassing the traditional path entirely. No CS degree required. No algorithms PhD needed. No leetcode grinding for 2 years.

But here's the reality: This roadmap only works if you follow the exact sequence with unwavering dedication, and have the right mentors to guide you when you're stuck.
97% of self-learners quit within 3 months. Not because the roadmap is wrong, but because they're learning alone. No one to review their code. No one to explain why their authentication logic fails. No one to push them through the inevitable "I don't understand this" moments.
That's where STEM Link's Software Engineering Professional Certification changes everything.
It's 8 months of intensive mentorship from 20+ working industry professionals: CTOs coaching you in building Industry Grade products, senior engineers reviewing your projects, tech leads guiding your externships, and career coaches preparing you for interviews.
And we back it with something no university or institute in Sri Lanka has ever done: a 100% Paid Job Placement Guarantee.
This roadmap has been refined through 500+ hours of feedback from students, CXOs, and hiring managers. The learning sequence is deliberate. The project choices are strategic. The interview prep is comprehensive.
PHASE 1: FOUNDATIONS - PROGRAMMING & WEB DEVELOPMENT (Months 1-3)

What: Python + HTML/CSS/JavaScript + Data Structures Fundamentals
Why: Build your programming brain while learning to create for the web
The Big Picture:
These first 3 months aren't about memorizing syntax or collecting certificates. You're learning to think like an engineer, breaking down complex problems into logical steps, understanding how data flows through systems, and building things people can actually use.
You'll split your time between two parallel tracks: learning programming fundamentals with Python, and building interactive websites with HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. By Month 3, you'll understand both how computers think and how the web works.
Track A: Programming Fundamentals with Python
Why Python? It's the closest programming language to plain English, used by Google, Netflix, and Instagram for their backends, and teaches you core concepts that transfer to every other language.
What You're Really Learning:
Problem-Solving Through Code:
Variables, loops, functions, and conditional logic aren't just syntax, but they're how you teach computers to automate repetitive work. Think processing 10,000 bank transactions in seconds instead of manually, or scraping 500 job postings and filtering by salary range automatically.
Working with Data:
You'll master Python's data structures (lists, dictionaries, sets) and learn when to use each. The difference between using a list vs a dictionary can mean the difference between your code running in 1 second or 10 minutes. You'll also handle files, like reading CSVs, processing JSON from APIs, managing user data.
Object-Oriented Thinking:
Instead of writing messy spaghetti code, you'll learn to organize programs into logical units (classes and objects). Think of it like this: a BankAccount class knows how to deposit, withdraw, and check balance. You create that blueprint once, then instantiate it for every customer. This is how professional software scales.
Real Applications You Can Build:
Expense tracker CLI that saves data to files
Web scraper that pulls job listings from multiple sites
Data analysis tool that processes CSV files and generates reports
Automation scripts that handle repetitive tasks
Track B: Web Development - HTML, CSS, JavaScript
The Three Layers of the Web:
Every website you've ever used is built with these three technologies working together. HTML provides structure, CSS creates visual design, and JavaScript makes it interactive. Master these, and you can build anything from landing pages to full web applications.
HTML - The Skeleton:
Learn semantic HTML (using the right tags for the right purpose), forms and input handling, and accessibility principles. This isn't just it, but proper HTML affects your Google rankings, makes sites usable for people with disabilities, and determines whether your forms actually work.
CSS - The Visual Layer:
Master layout systems (Flexbox for one-dimensional layouts, Grid for two-dimensional), responsive design (making sites work on phones, tablets, and desktops), and modern styling with Tailwind CSS. Good design isn't decoration, but it's the difference between users trusting your site or leaving in 3 seconds.
You'll learn why Netflix's horizontal scrollers use Flexbox, how Pinterest creates its masonry layout with Grid, and why 60% of web traffic being mobile means you must think mobile-first.
JavaScript - The Behavior:
This is where websites come alive. When you click "Add to Cart" and the number updates without refreshing, and that's JavaScript. When Google autocompletes your search as you type, that's JavaScript too.

You'll master DOM manipulation (changing webpage content on the fly), event handling (responding to clicks, scrolls, inputs), ES6+ modern features (the syntax professionals actually use), and asynchronous programming (handling API requests without freezing the page).
Critical Concept - Async JavaScript:
Network requests take time. You can't freeze the entire page waiting for data. You'll learn Promises and async/await, which is the modern way to handle operations that take time. This is foundational for everything in web development.
Projects You can Build:
Responsive portfolio website that looks perfect on all devices
Weather dashboard pulling real-time data from APIs
Interactive to-do app with localStorage (data persists after refresh)
Image gallery with search, filtering, and lightbox effects
Form with real-time validation and error handling
Track C: Data Structures & Algorithms (Running Throughout Months 1-3)
Why This Can't Be Skipped:
Most beginners think, "I'm building websites, why do I need algorithms?" Here's why: Every technical interview tests this. Every performance problem comes down to this. Every senior engineer knows this.
The Holistic View:
Data structures are containers for organizing information. Algorithms are step-by-step procedures for solving problems. Together, they determine whether your app loads in 0.5 seconds or crashes under load.
What You're Learning and Why It Matters:
Arrays, Strings, and Hash Tables:
These are your fundamental data containers. You'll learn when to use each, how searching works (linear vs binary), and why hash tables give you instant lookups. Real impact: Finding a user among 1 million records in milliseconds instead of minutes.
Linked Lists and Recursion:
Linked lists teach you about pointers and dynamic memory. Recursion teaches you to break big problems into smaller identical problems. Real applications: File system navigation (folders within folders), undo/redo functionality, tree traversal algorithms.
Stacks and Queues:
Stacks power your browser's back button and undo features (Last-In-First-Out). Queues manage print jobs and customer support tickets (First-In-First-Out). You'll implement both and understand when each is appropriate.
Sorting and Searching:
You'll implement bubble sort, selection sort, and understand why they're slow (O(n²)). Then you'll learn why merge sort and quick sort are used in production (O(n log n)). You'll master binary search and understand why sorted data enables fast lookups.
Big O Notation:

This is how engineers communicate efficiency. O(1) means instant regardless of data size. O(n) means time scales linearly. O(n²) means your algorithm will choke on large datasets. You'll learn to analyze your code and optimize intelligently.
The Real-World Use Cases:
Instagram feed: Array of posts with efficient searching
Netflix recommendations: Graph algorithms analyzing connections
Google Maps: Shortest path algorithms (covered later in Month 5-6)
E-commerce sorting: Quick sort algorithms organizing thousands of products
Password validation: String algorithms checking patterns
Shopping cart: Hash tables for instant product lookups
Practice Approach:
You'll solve 3-5 coding problems weekly on platforms like LeetCode and HackerRank, starting with Easy problems and progressing to Medium. The goal isn't to memorize solutions, but it's to recognize patterns and develop problem-solving intuition.
By the end, you'll have:
Built 5-8 complete projects (portfolio-ready)
Solved 40-60 algorithmic problems
Understanding of how data flows from frontend to backend
The foundation to learn any framework or technology
PHASE 2: FRONTEND ENGINEERING (Month 4)
What: React + Next.js + Modern UI + Version Control + Data Structures Level 2
Why: Building professional user interfaces the way real companies do
The Shift: From Vanilla JavaScript to Professional Frontend
Month 3 ended with you building interactive websites using HTML, CSS, and vanilla JavaScript. Month 4 is where you learn how actual tech companies build scalable user interfaces.
The reality: building a simple to-do app with vanilla JavaScript is doable. Building Facebook's news feed, Netflix's dashboard, or an e-commerce platform? Vanilla JavaScript becomes unmaintainable chaos. That's why 60%+ of frontend jobs require React, it's the industry solution to building complex UIs.
React - Component-Based Architecture

The Core Problem React Solves:
When your UI gets complex (think 50+ interactive elements, real-time updates, user authentication, shopping carts), vanilla JavaScript forces you to manually track every piece of state, update every DOM element, and manage every event listener. One bug and the entire app breaks.
React introduces component-based architecture: break your UI into independent, reusable pieces. A Button component. A ProductCard component. A Navbar component. Each manages its own logic. You compose them like LEGO blocks to build entire applications.
What You'll Master:
JSX and Components:
Write HTML-like syntax inside JavaScript. Instead of document.createElement() hell, you describe what you want: <button onClick={handleClick}>Submit</button>. React handles the rest.
State and Props:
Props pass data from parent to child (think function parameters). State manages data that changes over time (form inputs, toggles, counters). When state updates, React automatically re-renders only what changed—no manual DOM manipulation.
Hooks - The Modern React Paradigm:
React Hooks (useState, useEffect, useContext, useReducer) are functions that let you manage state, side effects, and component lifecycle. You'll learn when to use each, how to build custom hooks for reusable logic, and how to avoid common pitfalls like infinite loops.
Real Applications:
Dashboard that fetches and displays real-time data
Shopping cart that persists across page navigation
Multi-step form with validation and error handling
Search interface with debouncing and API integration
Modern UI with Shadcn/ui and Tailwind CSS
Why This Matters:
Users judge your application in under a second. A beautiful, responsive UI isn't optional, it's the difference between getting hired and getting ignored. Companies want developers who can build production-ready interfaces, not tutorial clones.
React Router - Multi-Page Applications
Single-page applications (SPAs) still need navigation. React Router handles client-side routing, with no page refresh when users navigate between Home, Products, Dashboard, Profile. You'll implement:
State Management - Scaling Beyond Component State
The Problem:
When your shopping cart needs to be accessible on 10 different pages, passing props through 7 levels of components becomes absurd. When user authentication status determines what every component displays, managing state gets complex.
The Solutions:
Zustand (Client State): Lightweight global state management.
RTK Query (Server State): Fetching data from APIs, caching responses, handling loading/error states, and keeping data fresh across your app
Next.js - The Production Framework

Why Next.js Exists:
React is a library for building UIs. But production apps need routing, API endpoints, SEO optimization, image handling, and deployment strategies. Next.js is the complete framework that adds all of this to React.
Where It's Used:
TikTok, Twitch, Nike, Hulu, Notion, and thousands of startups. If you're building a production React app in 2025, you're using Next.js.
TypeScript - Type Safety for Scalable Code

Why TypeScript?
JavaScript is dynamic but error-prone at scale. TypeScript adds static types, catching bugs at compile time. Used by 90%+ of professional React/Next.js teams.
What You'll Master:
Type annotations, interfaces, generics
Type-safe props and state in React components
Handling API responses with typed data
Real Impact: Eliminates "undefined is not a function" runtime crashes. Makes refactoring safe across large codebases.
Version Control with Git and GitHub - The Professional Standard

Critical Reality Check:
No company will hire you without Git knowledge. Not knowing Git in 2025 is like not knowing email in 2010. It's not optional.
Why Version Control Matters:
Collaboration:
Five developers working on the same codebase without overwriting each other's work. Reviewing code before it goes to production. Tracking who changed what and why.
Safety Net:
Made a mistake? Revert to last working version in 10 seconds. Want to try a risky experiment? Create a branch, test, merge if successful, delete if failed.
Your Portfolio:
Your GitHub profile is your public resume. Recruiters check your contribution graph, read your code, and evaluate your commit quality before calling you for interviews.
Data Structures & Algorithms - Level 2: Trees and Recursion
Binary Trees and Traversals:
How to navigate tree structures (inorder, preorder, postorder, level-order). When to use each. Why recursion is the natural approach for tree problems.
Binary Search Trees (BST):
Organized trees where left child < parent < right child. Real applications: Database indexes, autocomplete systems, efficiently storing sorted data.
Tree Problems:
Maximum depth, validating BSTs, lowest common ancestor, path sum problems. These aren't random, they appear in 20% of technical interviews.
Recursion Mastery:
You started with simple recursion in Month 3. Now you'll tackle tree recursion, backtracking problems, and divide-and-conquer algorithms. This is where algorithmic thinking deepens.
Real Projects You Can Build This Month:
1. Project Management Dashboard (React + Zustand):
CRUD operations (Create, Read, Update, Delete tasks)
Filters and sorting
Global state management
Responsive UI with Tailwind
2. E-Commerce Product Catalog (Next.js):
Server-side data fetching
Product listing and detail pages
Search and filtering
Shopping cart with Zustand
Image optimization
3. Weather Dashboard + Analytics (React + API Integration):
Real-time data from OpenWeather API
Search by city
5-day forecast display
Loading and error states
Dark mode toggle
PHASE 3: BACKEND ENGINEERING (Months 5-6)
What: Node.js + PostgreSQL + Authentication + APIs + Data Structures Level 3
Why: Building the engine that powers everything—data, security, and scalability
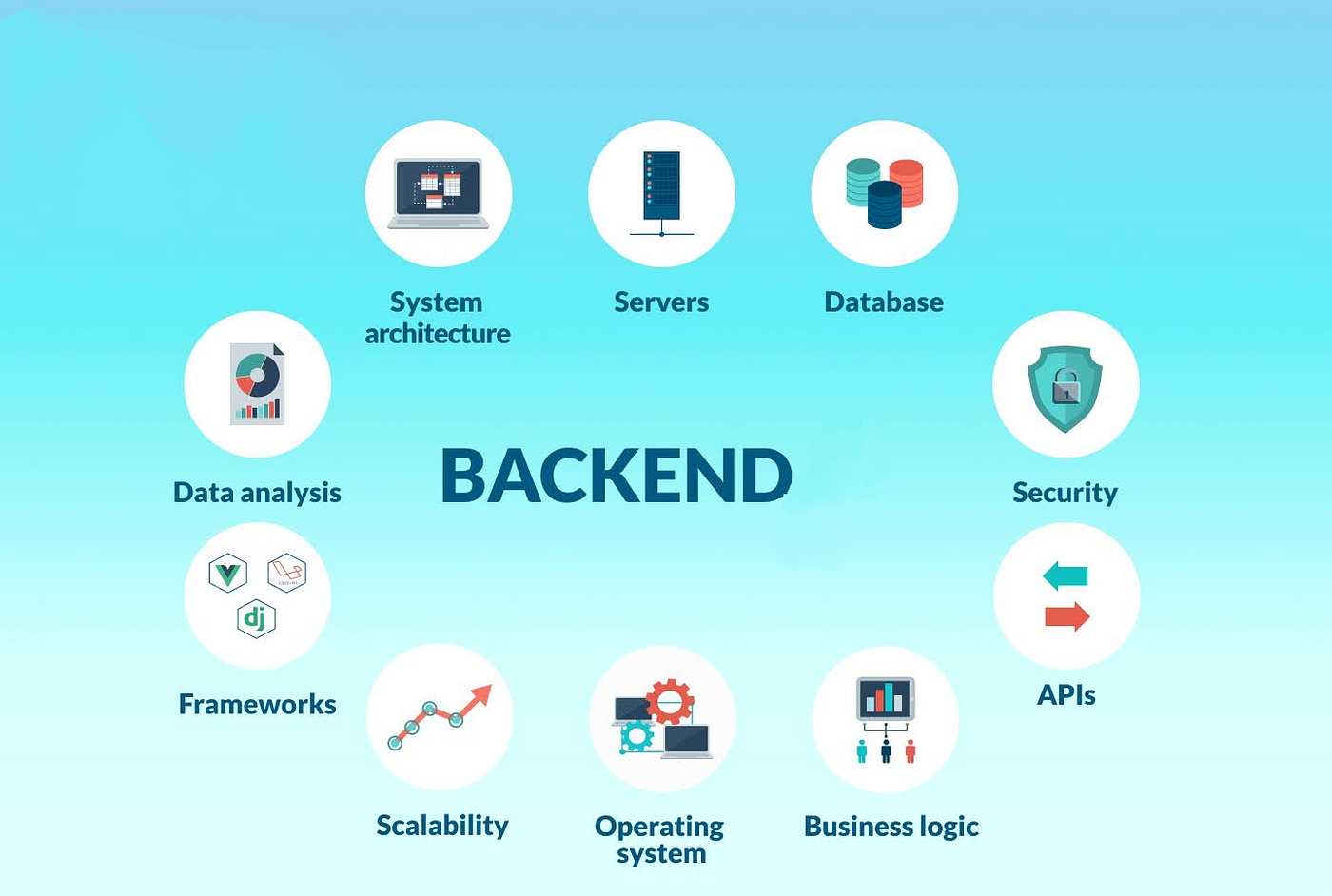
The Backend Reality:
Frontend is what users see. Backend is what makes everything work. When you buy something on Amazon, the backend processes your payment, updates inventory, sends confirmation emails, and initiates shipping, all in milliseconds. Companies might compromise on UI polish. They will never compromise on backend security or reliability.
These two months transform you from someone who builds interfaces to someone who builds complete systems.
Node.js and Express - Building the Server

Why Node.js?
It's JavaScript running on servers instead of browsers. Same language for frontend and backend means you can move seamlessly between both. More importantly, Node.js uses an event-driven, non-blocking architecture—handling thousands of concurrent requests without breaking a sweat. This is how Netflix streams to millions of users simultaneously.
What You'll Build:
REST APIs:
The communication layer between frontend and backend. You'll create endpoints that handle requests:
POST /api/users/register- Create accountsPOST /api/users/login- Authenticate usersGET /api/products- Fetch product listingsPOST /api/cart/add- Add items to cartDELETE /api/cart/:id- Remove items
Middleware:
Functions that run before your main logic—logging requests, checking authentication, validating data, handling errors globally. Professional backends are built on well-structured middleware chains.
Real Project:
By week 2, you'll have a fully functional REST API handling user authentication, CRUD operations, and error handling. Deployed and accessible via public URL.
PostgreSQL - Where All Data Lives
Why PostgreSQL?
It's open-source, battle-tested (used by Instagram, Reddit, Spotify), and handles everything from small apps to systems managing billions of records. Relational databases organize data in tables with relationships, for an example users have orders, orders have items, products belong to categories.
SQL Mastery:
Core Operations:
CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) is the foundation. We should be able to add new data to database, and for the existing data, we should be able to read, edit and write them. But real applications need more.
Advanced Querying:
JOINs let you combine data from multiple tables in a single query, like fetching users with their orders and order details efficiently. Aggregate functions (COUNT, SUM, AVG) answer business questions: "How many users registered this month?" "What's our total revenue today?" "Which categories sell best?"
Database Design:
Before writing any SQL, you design your schema. What tables do you need? What relationships exist between them? Normalization ensures you're not duplicating data wastefully. Indexes speed up searches on large datasets (think finding one user among 10 million records instantly).
Transactions:
When operations must succeed or fail together like transferring money (deduct from Account A, add to Account B), where transactions guarantee atomicity. If the server crashes mid-operation, the entire transaction rolls back. No partial updates, no corrupted data.
Prisma ORM:
Instead of writing raw SQL for every query, Prisma gives you a type-safe query builder. Define your schema once, Prisma generates the client code. Migrations, relationships, and complex queries become manageable. This is how professional teams work with databases.
Authentication and Security - The Non-Negotiable Part
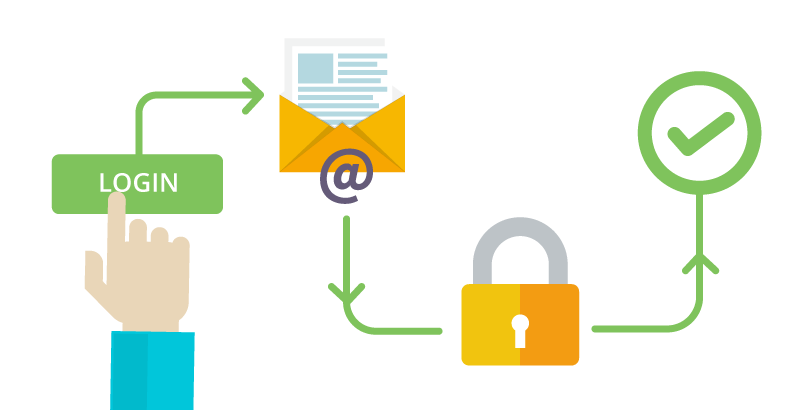
JWT (JSON Web Tokens):
How login actually works: user submits credentials (email, password) → server validates → returns JWT token → client includes token in subsequent requests → server verifies token. This is how you stay logged in across pages, how mobile apps maintain sessions, how APIs know who's making requests.
Clerk/Firebase Integration:
Building authentication from scratch is a security minefield. Clerk or Firebase kind of services handles social logins, email verification, password resets, session management, and provides a user management dashboard. You integrate it, customize it, but don't reinvent it.
Security Best Practices:
Never store plain-text passwords (hash with bcrypt). Validate all user input (never trust data from clients). Prevent SQL injection with parameterized queries. Implement rate limiting to stop spam and DDoS attacks. Configure CORS properly so only your frontend can access your API.
Role-Based Access Control:
Admins can delete users. Regular users cannot. Middleware checks roles before allowing operations. This is standard in every production application.
Third-Party Integrations - Real Production Features
File Uploads:
Users upload profile pictures, documents, images. You handle these with Multer, then store them on AWS S3 or Cloudinary (not on your server—doesn't scale).
Email Services:
SendGrid or Resend sends verification emails, password resets, order confirmations. You trigger emails programmatically, they handle delivery.
Payment Processing:
Stripe handles credit cards securely (PCI compliance is complex—let Stripe manage it). You integrate their API, create payment intents, handle webhooks when payments succeed or fail. This is how e-commerce actually works.
DevOps & Deployment
Docker Containerization: Package apps consistently across dev, staging, production. One Dockerfile works everywhere.
Cloud Platforms (Vercel/AWS):
Vercel: Frontend deployment, previews per PR
AWS: Scalable backend hosting (EC2, Lambda)
Dockerize full-stack app
Deploy to Vercel + AWS
Advanced Backend Patterns
Microservices Introduction: Break monoliths into focused services communicating via APIs.
Redis Caching: Store frequent queries (user sessions, API responses) for sub-100ms responses.
GraphQL Alternative: Query exactly what you need, reduce over/under-fetching vs REST.
Data Structures & Algorithms - Level 3: Graphs and Advanced Problem-Solving
Why Graphs Matter:
Social networks are graphs (people connected by friendships). Google Maps is a graph (cities connected by roads). YouTube recommendations are graphs (videos connected by viewing patterns). LinkedIn connections, citation networks, web page links—all graphs.
What You'll Master:
Graph Traversal:
BFS (Breadth-First Search) finds shortest paths in unweighted graphs—LinkedIn's "degrees of separation," Facebook's friend suggestions. DFS (Depth-First Search) solves mazes, detects cycles, performs topological sorting.
Shortest Path Algorithms:
Dijkstra's algorithm finds the fastest route on Google Maps. Given 50 possible routes with varying traffic conditions (weighted edges), it calculates the optimal path. This isn't theoretical—this powers GPS navigation, network routing, and logistics optimization.
Advanced Data Structures:
Heaps and Priority Queues:
Hospital ERs use priority queues (critical patients first). Operating systems use heaps for task scheduling. Dijkstra's algorithm relies on min-heaps for efficiency. You'll implement these and understand their O(log n) operations.
Hash Maps at Scale:
Understanding collision handling, load factors, and when to resize hash tables. Database indexes use hash structures for O(1) lookups across billions of records. Caching systems (Redis, Memcached) are built on hash tables.
Dynamic Programming Introduction:
Breaking complex problems into overlapping subproblems. You'll solve classic problems (Fibonacci, coin change, climbing stairs) and understand real applications: autocorrect algorithms (edit distance), stock trading strategies (maximum profit), resource allocation (knapsack problem).
Practice Routine:
4-5 graph and DP problems weekly. Focus on recognizing when to use BFS vs DFS, understanding graph representations, and building dynamic programming intuition. These categories appear in 30%+ of technical interviews.
Real Projects You Can Build:
Full-Stack Integration
Connect your Month 4 frontend to Month 5-6 backend
Deploy complete application
Authentication flow working end-to-end
Payment processing live
Production-ready with proper error handling
PHASE 4: OBJECT-ORIENTED PROGRAMMING (Month 7)
What: Java + OOP Principles + SOLID + Advanced Tree & Graph Algorithms
Why: Enterprise-level code design and advanced problem-solving

Why Java and OOP Matter:
You've been writing JavaScript and Python—languages that let you code however you want. Month 7 introduces strict object-oriented programming with Java, the language powering banks, airlines, government systems, and Android apps on billions of devices.
Why this matters for your career:
Enterprise companies (the ones with big budgets and stability) use Java. More importantly, OOP principles—encapsulation, inheritance, polymorphism, abstraction—appear in every technical interview. Understanding OOP deeply separates mid-level engineers from juniors stuck at entry level.
The shift:
Java is compiled (catches errors before runtime), strongly typed (every variable has a declared type), and forces you to think in objects and classes. This discipline makes you a better engineer in any language.
Object-Oriented Programming - The Core Paradigm
What OOP Solves:
Imagine building a banking system with 50,000 lines of code using only functions and variables. Chaos. OOP organizes code into logical units (classes) that bundle data and behavior together. A BankAccount class knows its balance and how to deposit/withdraw. You create thousands of account objects from that blueprint, each managing its own state.
The Four Pillars:
Encapsulation:
Hide internal complexity, expose only what's necessary. You use an ATM without knowing its internal circuitry. Same with code—a class's internal data is private; you interact through public methods. Result: Prevents bugs (can't accidentally corrupt data), improves security, makes code maintainable.
Inheritance:
Child classes inherit properties and methods from parent classes. Vehicle parent → Car, Truck, Motorcycle children. Write common logic once in the parent, customize in children. Result: Code reusability, logical hierarchies, easier maintenance.
Polymorphism:
Same method name, different behavior based on object type. A PaymentProcessor has a process() method. Pass it a CreditCard object—charges the card. Pass it PayPal—processes PayPal payment. Pass it BankTransfer—handles bank transfer. Same interface, different implementations. This is how professional systems handle multiple payment methods, multiple database types, multiple notification channels.
Abstraction:
Define contracts (interfaces) without specifying implementation details. A Database interface says "you must implement connect(), query(), disconnect()" but doesn't care if it's MySQL, PostgreSQL, or MongoDB underneath. Result: Swap implementations without rewriting code, design systems before coding, create flexible architectures.
SOLID Principles - Writing Professional Code
These five principles separate amateur code from production-quality systems:
Single Responsibility:
Each class has one job, one reason to change.
Open/Closed:
Open for extension, closed for modification. Adding a new payment method shouldn't require changing existing payment code, but extend the system instead. This is how Netflix adds new content types without breaking existing streaming.
Liskov Substitution:
Subclasses should work anywhere their parent class works. If your code expects a Bird and you pass a Penguin (which can't fly), it breaks. The principle: design inheritance hierarchies carefully.
Interface Segregation:
Don't force classes to implement methods they don't need. A Printer interface with scan(), print(), fax() forces basic printers to implement fax functionality they don't have. Better: Separate interfaces for each capability.
Dependency Inversion:
Depend on abstractions (interfaces), not concrete implementations. Your e-commerce code depends on a PaymentGateway interface, not specifically on Stripe. Want to switch to PayPal? Just implement the interface—no core code changes.
Why This Matters:
Senior engineers talk in SOLID principles. Code reviews check for these. Interview questions ask you to refactor code violating SOLID. This isn't academic—this is how scalable systems are built.
Java Specifics - What You'll Master
Static Typing:
Declare types explicitly: int count = 0;, String name = "John";, List<Product> products = new ArrayList<>();. Catches type errors at compile time instead of runtime crashes.
Compilation:
Java compiles to bytecode that runs on the JVM (Java Virtual Machine). Write once, run anywhere—Windows, Mac, Linux, doesn't matter.
Real Projects:
Library management system (books, members, loans, late fees)
E-commerce order processing (products, carts, orders, payments)
Banking system simulation (accounts, transactions, transfers)
Task management with priority queues
By week 3, you'll:
Design class hierarchies, implement interfaces, apply SOLID principles, and understand why Java remains dominant in enterprise software despite being more verbose than Python or JavaScript.
Data Structures & Algorithms - Level 4: Advanced Trees and Graph Algorithms
Advanced Tree Structures:
Balanced Trees (AVL and Red-Black):
Regular Binary Search Trees can become unbalanced (degenerate into linked lists in worst case O(n) operations). Self-balancing trees maintain O(log n) guaranteed performance through rotations.
Real use: Database indexes use Red-Black trees
Tries (Prefix Trees):
Specialized trees for storing strings efficiently. Each node represents a character; paths form words. Applications: Autocomplete (type "app" → suggests "apple, application, apply"), spell checkers, IP routing in network routers, browser history search. Advantage over hash tables: Can find all words with a given prefix, naturally sorted, no collision handling.
Advanced Graph Algorithms:
Dijkstra's Algorithm - The Practical One:
Finding shortest paths in weighted graphs. Real applications: Google Maps calculates fastest route considering traffic (edges have weights representing time/distance). Flight booking finds cheapest multi-hop routes. Network routing optimizes packet paths across the internet.
How it works: Start at source, explore neighbors, always pick the unvisited node with smallest known distance, update neighbor distances. Uses a min-heap for efficiency. Time complexity: O((V + E) log V).
Bellman-Ford:
Handles graphs with negative edge weights (Dijkstra can't). Real use: Currency exchange arbitrage detection—finding profitable cycles in exchange rates.
Real Projects You Can Build:
1. Banking System (OOP Design):
Account hierarchy (Savings, Checking, Business)
Transaction processing with ACID guarantees
Role-based permissions (Customer, Teller, Manager)
Interest calculation and fee management
2. Task Scheduler (Advanced Algorithms):
Priority queue implementation
Dependency resolution with topological sort
Deadline scheduling
Resource allocation optimization
PHASE 5: TESTING, DEPLOYMENT & ADVANCED DSA (Month 7-8)
What: Professional Development Practices + Expert-Level Algorithms
Why: Production-ready code that scales
Testing - The Professional Requirement:
Why Testing Matters:
Reality Check: Companies won't hire you without testing knowledge
Cost of Bugs: Facebook's 2021 outage cost $100M. Testing prevents this
Confidence: Deploy on Friday without fear
Unit Testing:
What: Testing individual functions in isolation
Example: Testing if
calculateTotal()returns correct sumTools: Jest, Vitest
Real Practice: Every function you write gets a test
Integration Testing:
What: Testing how components work together
Example: Does login form → API → database work end-to-end?
Real World: Testing checkout flow (cart → payment → confirmation)
End-to-End Testing:
What: Testing entire user workflows
Tools: Playwright, Cypress
DevOps & Deployment:
Version Control - Git Mastery:
Beyond Basic Commits:
Branching strategies (Git Flow, GitHub Flow)
Feature branches, pull requests
Code review process
Resolving merge conflicts
Rebasing vs merging
CI/CD Pipelines:
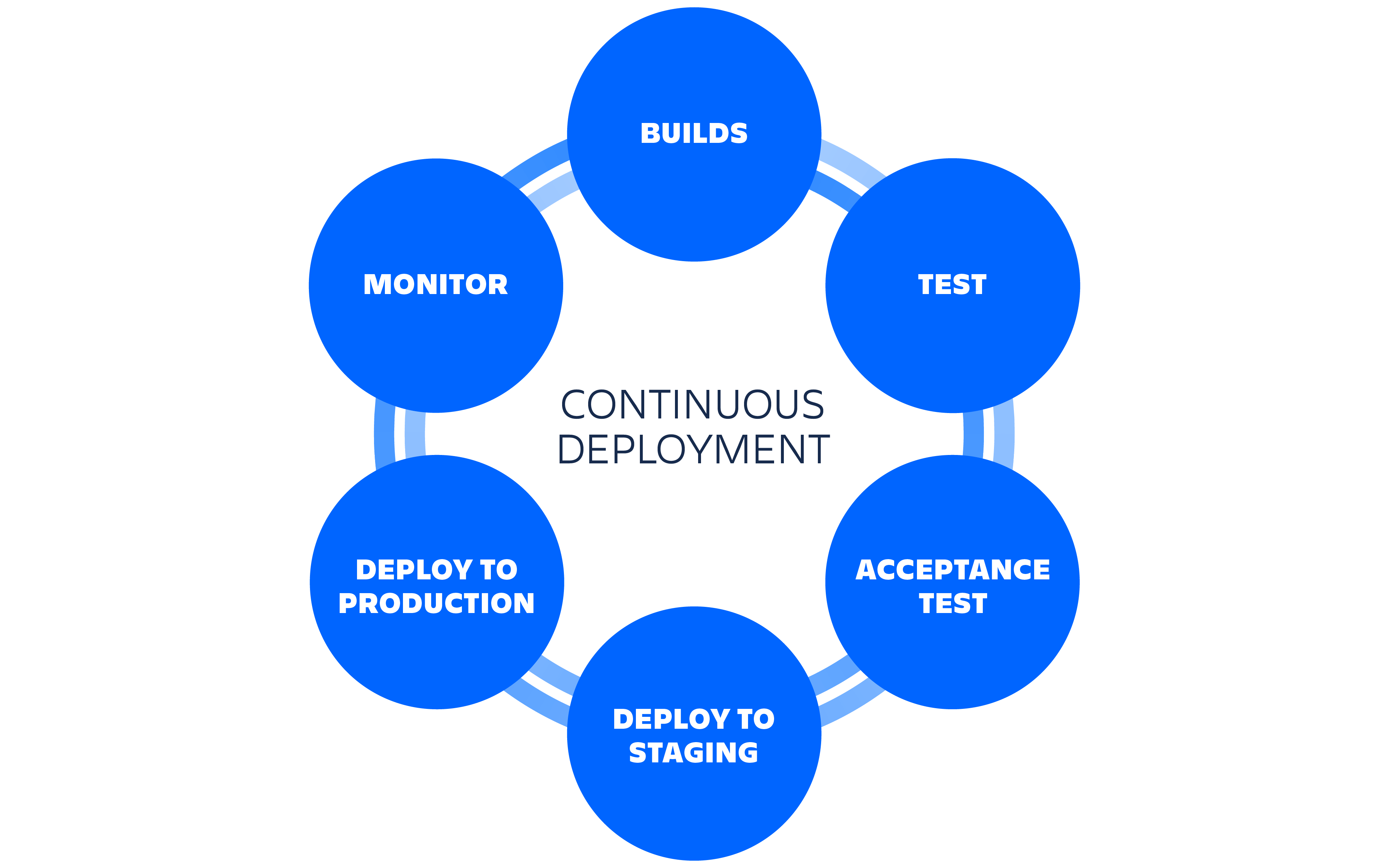
Continuous Integration: Automated testing on every commit
Continuous Deployment: Automated deployment when tests pass
GitHub Actions:
Run tests automatically
Deploy to production
Notify team on failures
Real World: Push to main branch → tests run → if pass, deploy to production. All automatic.
Environment Management:
Development, Staging, Production: Separate environments
Environment Variables: Secrets, API keys, database URLs
Security: Never commit secrets to Git
Data Structures & Algorithms - Level 5: Expert-Level Problem Solving
Advanced Dynamic Programming:
Classic DP Problems
Matrix Chain Multiplication
Backtracking Algorithms
N-Queens Problem
Sudoku Solver
Greedy Algorithms
PHASE 6: The Final Sprint - Getting Hired (Month 8)
Month 8 is not about learning new technologies. It's about packaging everything you've built and proving your skills to employers.
Part A: Building Your Professional CV
What Goes In Your CV:
1. Projects Portfolio (Most Critical Section):
Include projects demonstrating full-stack capabilities:
Full-Stack Applications:
Complete SaaS platform (authentication, database, deployment)
Social platform clone with user profiles and interactions
Booking/reservation system with email notifications
2. Algorithmic Problem-Solving Achievements:
- Solved 150+ problems across LeetCode, HackerRank (50 Easy, 75 Medium, 25 Hard)
- Implemented optimized solutions for graph traversal, dynamic programming, tree algorithms
3. Real Client Work / Externship Experience
Part B: Interview Preparation - Two-Pillar Approach
Pillar 1: Hands-On Full Stack Engineering Implementation
Project Deep-Dive Questions (30-45 minutes):
Interviewers don't ask you to build an entire feature from scratch. They ask you to explain, defend, and discuss the projects you've already built. They're evaluating whether you truly understand what you built or just followed tutorials.
Typical Questions About Your Projects:
Architecture and Design:
"Walk me through the architecture of your e-commerce application"
"Explain how authentication works in your application end-to-end"
"How does data flow from frontend to backend in your app?"
Technical Implementation:
"How did you implement file uploads? Where are files stored?"
"Explain your database schema for the order management system"
"What security measures did you implement?"
"How do you prevent SQL injection in your API?"
Problem-Solving and Trade-offs:
"What was the hardest technical challenge you faced? How did you solve it?"
"If you had to scale this app to 10,000 concurrent users, what would you change?"
"What would you do differently if you rebuilt this project?"
Code Quality and Best Practices:
"How did you structure your codebase? Why that folder structure?"
"How do you validate user input on both frontend and backend?"
"What testing approach did you use?"
Pillar 2: Software Engineering Fundamentals
Master These Three Areas:
1. SQL & Database Management:
Practice Live Queries:
Join multiple tables to fetch related data
Aggregate functions (COUNT, SUM, AVG with GROUP BY)
Subqueries and CTEs for complex data retrieval
Find top N records, rankings, duplicates
Conceptual Questions:
"Explain ACID properties and why they matter"
"When should you use an index? Trade-offs?"
"Difference between INNER JOIN and LEFT JOIN with example"
"How do you prevent SQL injection?"
"Normalization vs denormalization - when to use each?"
Resource: Solve 50+ SQL problems on LeetCode SQL section
2. Object-Oriented Programming:
Core Concepts You Must Explain:
Encapsulation with real-world analogy
Inheritance vs Composition - when to use which
Polymorphism with concrete example
Abstract classes vs Interfaces
SOLID principles with practical applications
Coding Exercises:
Design a library management system (classes, relationships)
Model a parking lot with different vehicle types
Implement a deck of cards with shuffle and deal methods
Design an e-commerce order system (orders, items, payments)
Practice: Explain each OOP concept to someone non-technical
3. Data Structures & Algorithms - Live Coding:
Master These Problem Categories:
Arrays & Strings (30%):
Linked Lists (15%):
Trees & Binary Search Trees (20%):
Sorting & Searching (15%):
Graphs (10%):
Dynamic Programming (10%)
The Path Forward: From Roadmap to Reality
This 8-month roadmap works, but only if you have expert guidance when you're stuck, code reviews from senior engineers, and real company projects to build.
That's exactly what STEM Link's AI-Powered Software Engineering Professional Certification provides: 20+ industry professionals coaching you daily, company externships with real teams, and a 100% Job Placement Guarantee, the first program in Sri Lankan education history to legally guarantee you get hired.
Software Engineering (AI-Powered) Professional Certification
Ready to Start Your Transformation?
Only 35 seats available for the January 2025 cohort.
We maintain small cohorts to ensure every student gets personalized mentorship from our 20+ industry professionals. When seats fill, the next cohort starts in 4 months.
Application closes when we reach 35 committed students, not on a calendar date.
If you're serious about becoming a software engineer in 8 months, this is your moment.
Apply Now - January 2025 Cohort →
Applications reviewed within 48 hours. Qualifying applicants receive interview invitations.
You may also like
How Anthropic's Claude AI Was Used in the U.S.-Israel Bombing of Iran
Anthropic’s Claude models almost certainly played a central role in Operation Epic Fury fusing intelligence, validating targets with strict ROE guardrails, running thousands of war-game simulations, and enabling real-time adaptive planning. Despite the public ban, deep classified integration made abrupt removal impractical, highlighting frontier AI’s irreversible shift into modern warfare
Anthropic Just Lost $200 Million to Pentagon
Anthropic had a $200 million Pentagon deal and lost it in days. They were marked a national security threat, while OpenAI swoops in for the same deal.
How “Agentic Employees” Are Quietly Wiping Out Entire Industries in the Last 48 hours?
The jobs everyone said were "AI-proof" are vanishing. And most people still haven't noticed what quietly happened in the last 48 hours. How can you survive this market?


